An incredible feat of biological engineering, the human eye is able to adapt to a wide variety of different light situations. The process of dilatation and constriction of the pupils is widely recognized as one of the most important mechanisms that enable this adaptation. In this exclusive blog post, we will learn the process of dilation of the eye & how long dilation eyes last. To bring an expert perspective into the topic, we got medical inputs from one of the finest eye specialists in Jalandhar -Dr Sanjeev from Duggal Eye Hospital Jalandhar in Punjab.
What happens during Eye Dilation
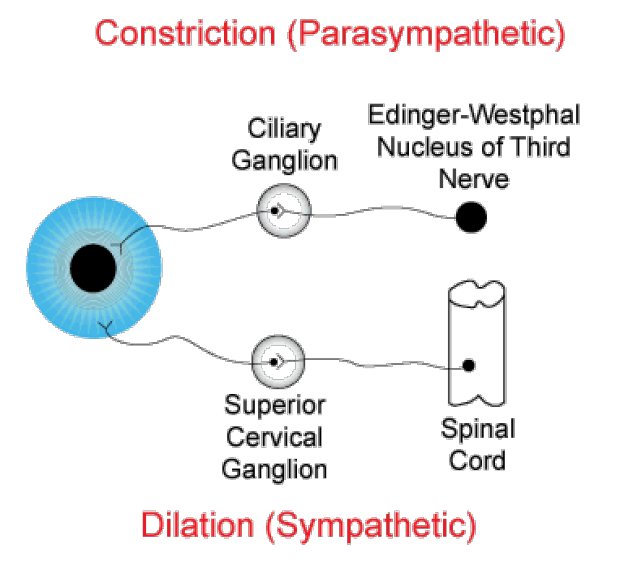
Eye dilation, or mydriasis in medical terms, is a physiological response in which the pupil (the black circle in the middle of the eye) gets bigger so that more light can get in. A muscle in the eye called the dilator pupillae controls this. It contracts when it gets signals from the nervous system. This usually happens when there isn’t much light, when someone is feeling very emotional, or when they are taking certain drugs or medicines.
Constriction, or miosis, is the opposite of dilation. This is when the pupil gets smaller to let less light into the eye. The sphincter pupillae muscle helps with this. It contracts when the parasympathetic nervous system tells it to. This generally happens in excessively bright light conditions or when you focus on something close up.
Dilation of the Eye - Means for Comprehensive Eye Examinations
One of the most common procedures that is carried out during eye examinations is called dilation of the eye. It is accomplished with the application of specialized eye drops that force the pupil, which is the dark area located in the middle of the eye, to grow larger. This increases the amount of light that can enter the eye, allowing the retina, macula, and optic nerve to be seen more clearly, among other interior structures of the eye.
Why is Dilation of the Eye required & helpful?
Dilation, an application of a series of eye drops, is an integral part of a complete eye exam because it lets doctors find common eye diseases and conditions that they might not be able to see during a regular test. Some of these are:
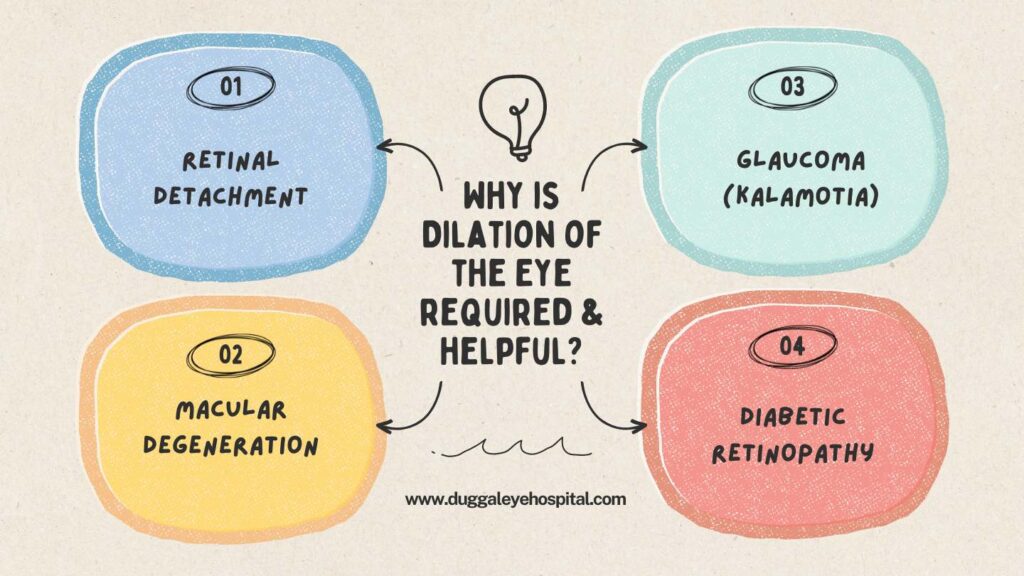
- Retinal Detachment: When the retina splits apart from the surrounding tissue, it is known as retinal detachment. It’s a serious eye disease. If you don’t get timely treatment for it, you may develop irreparable blindness.
- Glaucoma (Kalamotia): This disease affects the optical nerve that connects to the eyes, which can lead to vision loss or even blindness. A dilated eye test can help devise treatment at an early stage to prevent it from getting worse.
- Macular degeneration This eye condition makes it hard to see clearly in the middle of your field of vision, which is vital for things like reading and driving. The macula, the area of the eye that provides fine detail vision, is the target of macular degeneration.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: A widely common eye disease that develops in people with diabetes and can make them potentially blind if not treated in time and by a qualified eye specialist. If the illness is diagnosed at an early stage, it can be managed better, and its progression can be slowed down.
What are the possible Side Effects of Eye Dilation?
The process of dilatation can produce momentary discomfort, such as sensitivity to light and difficulties focusing on close objects; however, these effects usually disappear after a few hours have passed. The advantages of early detection of eye disorders and diseases greatly outweigh the temporary discomfort that may be experienced despite the fact that the pain is only temporary.
Overall, dilatation is a crucial component of a complete eye exam that should not be overlooked. In spite of the fact that it may cause some discomfort in the short term, it makes it possible to identify eye disorders at an earlier stage when they are more amenable to treatment.
How Long Does Eye Dilation Last?
Medically induced dilation is meant for detailed eye checkups by giving doctors visual access to the posterior parts of the eye. The length of time that your eyes dilate lasts depends on what caused it. The pupils can get bigger or smaller very quickly in reaction to changes in light or emotions, and they only stay that way as long as the stimulus is there. When dilation is caused by medicine, like during an eye test, it can last a lot longer, up to two days.
Eye specialists use certain drops to make the pupils bigger, which allows them to have a clearer eye examination as they can see the back of the eye better after eye dilation. These drops have medicines in them, like tropicamide or phenylephrine, which make the dilator pupillae muscle contract and the sphincter pupillae muscle relax. This makes the eyes bigger. Depending on the medicine used and how the person reacts, these drops can have effects that last anywhere from 4 to 24 hours. During this time, the person may become more sensitive to light and have trouble focusing on close things.
When Dilation Indicates a Problem?
Pupil dilation is a regular eye response to some things, but dilation that lasts for a long time or for no apparent reason can be a sign of a severe health problem, like brain damage, a stroke, or drug use. If you notice any unusual changes in your pupils, it’s advised that you connect with your eye specialist to figure out the underlying causes.
Dilation of the Eye as a means for better eye examination
Our ability to see is greatly influenced by the intriguing and intricate physiological reaction known as eye dilation. “The ability of the human eye to dilate and constrict is a monument to its fantastic versatility, as it allows us to see in the dark, allows doctors to inspect our eyes, and can be used to convey deep emotion. As with other aspects of our health, it is advised to be aware of any unusual vision changes and, if needed, seek medical assistance that may include dilation of the eye,” says Dr. Sanjeev Duggal, one of the most famous doctors in Jalandhar city of Punjab.

